Bi-Weekly and Semi-Monthly. Two of the most popular payroll frequency options. However, these also tend to be the most confusing. Just looking at the two, they sound like the same thing. Yet each payment schedule has some key differences and choosing the right one is crucial. So let’s dive deeper into the differences between Semi-Monthly vs Bi-Weekly Payroll.
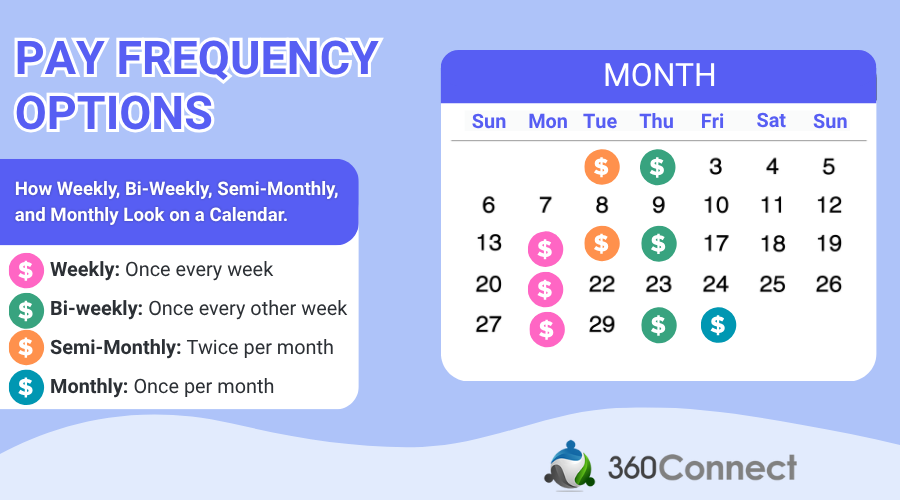
Before we get any further, it’s important to note there are four common types of payroll frequencies which are weekly, monthly, and the two we are discussing, bi-weekly and semi-monthly.
- Weekly: Once every week
- Monthly: Once per month
- Bi-Weekly: Once every other week
- Semi-Monthly: Twice per month
What is Semi-Monthly Payroll?
Semi-monthly payroll means paying employees twice a month on specific dates (e.g., 1st and 15th), totaling 24 pay periods a year.
In other words, semi-monthly basically means the payment is made and received twice a month. Typically, on fixed days like the 1st, 15th, or 30th of the month.
Typical Semi-Monthly Payroll (Example): If an employee earns $50,000/year salary under a semi-monthly schedule, they’d get \$2,083.33 each payday. (\$50,000/24)

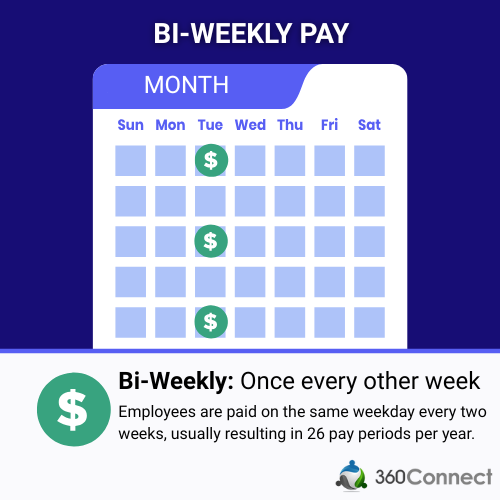
What is Bi-Weekly Payroll?
Bi-Weekly pay is when employees are paid every other week on a specific day.
For example, a bi-weekly pay frequency on a Thursday would mean employees get paid every other Thursday of the month. With bi-weekly payroll, employees are paid 26 paychecks a year, compared to 24 like bi-monthly receives.
Typical Bi-Weekly Payroll (Example): If an employee earns $50,000/year salary under a bi-weekly schedule, they’d get about \$1,923.08 each payday (\$50,000/26).
Side Note: Semi-weekly (twice a week) is different from bi-weekly (every two weeks), in this article, we focus on bi-weekly vs semimonthly.
How Pay Frequency Affects Overtime
If you have hourly employees, this one’s important. How you structure your pay schedule can make a big difference when it comes to calculating overtime, especially if you want to stay compliant and avoid payroll headaches.
Why Bi-Weekly Pay Works Better for Hourly Overtime
An hourly employee working 45 hours in a week would get all 5 overtime hours paid in the same bi-weekly paycheck, simple and straightforward. That’s because bi-weekly pay follows a consistent 7-day cycle, so any overtime worked in a single week gets bundled into that period.
But with semi-monthly payroll, the pay period doesn’t always align cleanly with the standard workweek. Say an employee works overtime the last few days of the month, that time might get split across two separate pay periods, depending on how your schedule is set up. That can lead to confusion, delayed OT payouts, and more manual work for your payroll team.
Long story short? Bi-weekly makes overtime easier to track, pay, and explain, especially if you’ve got a lot of hourly staff.
Semi-Monthly vs Bi-Weekly Payroll
Because semi-monthly and bi-weekly payroll are two of the most popular payroll frequencies, choosing between them will be difficult. Take a look at the differences, pros, cons, and statistics between the two to help narrow down your choice.

3 Key Differences Between Semi-Monthly vs Bi-Weekly Payroll
When comparing bi-weekly vs semi-monthly pay they may seem similar, but there are three key differences.
Key Differences Between Bi-Weekly and Semi-Monthly Pay
| Bi-Weekly | Semi-Monthly | |
| Pay Frequency | Every 2 weeks (26 paychecks/year) | Twice a month (24 paychecks/year) |
| Payday Schedule | Bi-weekly paydays fall on the same day of the week each period (e.g., every other Friday). | Semi-monthly paydays fall on specific dates (e.g., 15th and last day), which means the day of the week varies. |
| Paycheck Amount | Bi-weekly checks are smaller (since there are 26), but you get two extra checks in some months. | Semi-monthly checks are slightly larger on average, but only 24 per year. |

1. Payday
Bi-weekly payroll ensures employees receive their wages the same day every two weeks. Meanwhile, with semi-monthly, the day of the week can change. Semi-monthly payroll goes off of two dates in the month, generally the 1st and the 15th, thus the day it falls on per month can differ.

2. Amount of Paychecks per Year
As a result of the pay frequency difference between semi-monthly and bi-weekly payroll, semi-monthly employees receive 24 paychecks each year, while biweekly employees receive 26.

3. Paycheck Quantity
In semi-monthly frequencies, payroll is processed fewer times than biweekly, so employees’ paychecks are larger. Furthermore, biweekly paychecks are smaller, but employees will receive two extra paychecks to make up the difference. However, as it stands, the two differ in paycheck quantity.
Pros and Cons of Semi-Monthly vs Bi-Weekly Payroll
After learning the difference between semi-monthly and bi-weekly payroll, let’s look at the pros and cons of each.
Semi-Monthly Pay Pros
Easy to Understand
Because pay occurs on the same two days every month, it takes the guesswork out for employees. Employers do not have to hear “when do we get paid” because those days are solid. Having fixed paydays also allows employees to budget their finances effectively.
Saves Companies Money
Compared to a bi-weekly payroll, semi-monthly has significantly fewer pay periods. Which equates to reduced employee paychecks and company savings.
Aligns with Business Cycle
A notable benefit of this pay frequency option is that it aligns with the business cycle. Since employees get paid around the same time as the business makes money, it is easier to pay them on time.
Semi-Monthly Pay Cons
Not Suitable for Hourly Employees
Businesses with hourly employees or commission employees may not find a semi-monthly frequency is the best option. When overtime and specific hours need to be determined weekly, it can be challenging to adapt to this pay schedule. Since the commission and hourly wages need to be divided between two different pay periods, it can be difficult for employers to adjust without needing to do it separately.
Delayed Paychecks for New Employees
When it comes to Semi-Monthly payroll, new hires will typically need to wait 4-6 weeks before receiving their first paycheck. This depends on the day they started in comparison to the payment schedule. For example, if an organization pays based on the previous period like the 16th to the end of the month. Then, if an employee starts on the 1st, they wouldn’t be paid until the end of the month. Others may choose to pay for the hours worked currently until the 15th. Either way, the full paycheck will be delayed for many new employees on a this payroll cycle.
Inconsistency
Because semi-monthly pay is on two solid days per month, it can be inconvenient when holidays occur. If a payday falls on a federal holiday, or weekend, the payday will need to be pushed up. Or even back by a day or two. Meaning employees will need to keep this in mind ahead of time.
Semi-Monthly Payroll Pros & Cons
| Semi-Monthly Pros | Semi-Monthly Cons |
| Easy to Understand: Straightforward budget (same two dates every month) | Not Ideal for Hourly Employees |
| Saves Companies Money: Fewer payroll runs (saves processing cost) | Delayed Paychecks for New Hires |
| Aligns with Business Cycle: Syncs with monthly expense cycles | Inconsistency: Changing days (payday can fall on weekends/holidays, requiring adjustments) |
Bi-Weekly Pay Pros
More Paychecks
Although bi-weekly offers smaller paychecks each pay period compared to a semi-monthly pay schedule, it still equates to more paydays. This makes it easier for employees to save more money during certain months because they receive an additional paycheck. Additional paychecks can be very beneficial during the holiday season.
Overtime is Easy to Calculate
When businesses operate on a biweekly pay schedule, overtime pay is much simpler to calculate than when operating on a semi-monthly pay schedule. Because calculations take place every other week, it is easy to manage overtime accordingly.
Bi-Weekly Pay Cons
Uncertain Budget
Receiving up to two additional paychecks per month compared to a semi-monthly pay schedule is certainly a bonus for employees. However, for business owners, it can be a hassle. For months where additional planning was not put in place, a small business may not have sufficient funds for a three paycheck month compared to a two paycheck month.
Smaller Paychecks
Although more paychecks may be a pro to some, the drawback of the checks being smaller may be a con to others.
Bi-Weekly Payroll Pros & Cons
| Bi-Weekly Pros | Bi-Weekly Cons |
| More Paychecks: Employees get paid more often (helps savings and cash flow) | Uncertain Budget: Can complicate budgeting for employers during months with three pay periods |
| Overtime is Easy to Calculate: Simpler overtime calculation (each paycheck usually covers two standard workweeks) | Smaller Paychecks: Smaller individual paychecks might be a downside for some |
Frequency Requirement Note: Be aware of your state’s payday requirements. Many states mandate a minimum pay frequency (e.g., at least semimonthly for most employees). Always ensure your chosen schedule complies with state law.
What’s the Difference Between Bi-Weekly, Semi-Monthly, and Bi-Monthly Pay?
Let’s be honest, these terms get confusing fast. Plenty of people say bi-monthly when they really mean semi-monthly, and it’s not hard to see why. Although we’ve touched on this already, it’s worth clearing up one last time, because these terms get mixed up a lot.
Here’s the deal:
- Bi-weekly means every two weeks on the same weekday (like every other Friday).
- Semi-monthly means twice a month on set dates (like the 1st and 15th).
- Bi-monthly technically means every two months, but some people use it to mean twice a month, which is where the confusion starts.
To keep things simple and clear:
Use semi-monthly for twice-a-month pay, and bi-weekly for every two weeks’ pay.
Our Recommendation Between Semi-Monthly vs Bi-Weekly Payroll
We recommend you take the three key differences and pros and cons between semi-monthly vs bi-weekly payroll when making your decision.
Next, based on the differences between the two payroll frequencies, we recommend that if you have more hourly employees you go with bi-weekly payroll, and if you have more salary employees you choose semi-monthly payroll.
Finally, consider popularity. By far, bi-weekly payroll is the most popular option. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, 43% of employees are paid bi-weekly. Meanwhile, 27% receive their pay weekly, 19.8% semi-monthly, and 10% monthly.
Compare Payroll Solution Options
Now that you’ve determined which payroll frequency is right for you, it’s time to compare payroll solution options. Payroll is one of the most important aspects of running your business, yet shopping for payroll services and software can be confusing.
At 360Connect, we connect you with up to 5 FREE price quotes from pre-qualified suppliers.
Related:
- Payroll Services: A Buyer’s Guide
- In-House vs. Outsourced Payroll: Pros and Cons
- The 7 Best Payroll Providers
- Best Payroll for Small Business: Key Factors to Consider
- How to Switch Payroll Providers
- Payroll for Startups: A Beginner’s Guide to Getting It Right

