Asset tracking is the method of tracking physical assets that your company owns. This tracking is for company assets that are used by employees, customers, or any parties who have access to them. Assets tracking works by three main methods:
- Barcode labels that can be scanned
- GPS tags
- RFID tags
Using these tools, companies are able to track the movement of assets within an organization, the usage of these assets, and the information associated with them.
Types of Assets Typically Tracked
Asset tracking can encompass a wide range of physical and intangible assets. Some of the most common assets tracked:
- Machinery and Equipment: Includes heavy machinery, production equipment, tools, etc.
- Vehicles: These include company cars, trucks, forklifts, and other transportation vehicles.
- Electronics: Computers, tablets, smartphones, and other tech gadgets.
- Furniture and Fixtures: Furniture for offices and facilities, including desks, chairs, lighting fixtures, and other items.
This is different than inventory tracking, which is about products that need to be sold, these items are needed for daily usage for a company. This is how asset tracking works, think of a forklift for a maintenance department. While these assets used to be tracked on pen and paper, asset tracking has become far more advanced.
The Technology Behind Asset Tracking
Asset-tracking software is a digital solution for managing and monitoring the location, status, and other essential details of an organization’s assets. This software makes it easy to view where your assets are, who has them, and when they will be returned.
Key Features of Asset-Tracking Software
Data Collection and Storage: It records and saves data about each asset, such as location, maintenance records, and usage history.
Real-Time Tracking: Many asset-tracking software solutions interface with RFID, GPS, and barcode technologies to offer real-time position (specifically for GPS) and status updates.
Maintenance and Lifecycle Management: They frequently contain tools for scheduling maintenance, tracking repair histories, and managing the total lifecycle of equipment.
Reporting and Analytics: You can gain insights on how your assets are used, time frames, how often, and more with the data provided within asset tracking software.
Integration Capabilities: The software can often be integrated with other business systems, such as ERP or inventory management systems, for seamless data flow and enhanced operational efficiency.
How Asset-Tracking Software Powers Asset Management
Centralized Asset Database: This program creates a centralized repository for asset information, making it simple for the organization to access and manage data.
Enhanced Visibility and Control: The software improves visibility and control over assets by giving real-time data on asset location and status, minimizing the likelihood of loss or misplacement.
Efficiency and Productivity: Automated tracking and reporting save time and resources, allowing staff to focus on more vital activities rather than manual tracking.
Cost Management: Asset-tracking software assists in detecting unused equipment, minimizing over-purchasing, and optimizing maintenance schedules, resulting in better cost management. You can also sell unused assets that are a drain on your system.
Compliance and Security: The software supports and ensures regulatory compliance by maintaining correct records and aids in asset security.
Implementing Asset Tracking in Business
Implementing an asset-tracking system is a strategic process that involves careful planning and execution. You’ll most likely want to appoint someone to oversee this process and have a team to manage the asset tracking. Here’s a detailed breakdown of the steps and considerations involved to make asset tracking work:
Assessing Business Needs
Understand your goals for asset tracking, whether they are to reduce theft, improve maintenance, improve inventory management, or increase general efficiency. Conduct a thorough audit of existing assets to determine what needs to be tracked and why.
Choosing the Right Technology
Different tracking technologies may be required for different assets. For example, high-value equipment may require GPS tracking, whereas simple goods may be tracked using barcodes or RFID tags.
Developing an Implementation Plan
Create a phased strategy with specific timelines. Begin with a trial program to test the system before going full-scale. Budget for not only the initial setup expenditures but also recurring expenses such as maintenance and updates.
Training and Change Management
Conduct extensive training sessions for all employees who will be utilizing the asset tracking system. This will ensure that the asset tracking works properly and everyone has a good understanding to use it to its full potential.
Maintenance and Upgrades
Schedule frequent maintenance inspections to ensure that the system’s hardware and software are in good working order. Keep the program up to date to take advantage of the most recent features and security enhancements.
Asset Tracking
Learn MoreChallenges and Considerations in Asset Tracking
Integrating asset-tracking systems with existing IT infrastructure can be complex, especially in organizations with legacy systems. You’ll want to make sure your asset-tracking software can integrate with any existing systems you already have in place. Ensuring the accuracy and reliability of data collected by asset tracking systems is crucial. Inaccurate data can lead to poor decision-making and make asset tracking work less effectively.
Additionally, as your company grows, you’ll need a system that can grow with you. This will help you scale accordingly and help keep costs lower. Not to mention, as your system grows you’ll want to make sure you want your upkeep with the increased maintenance.
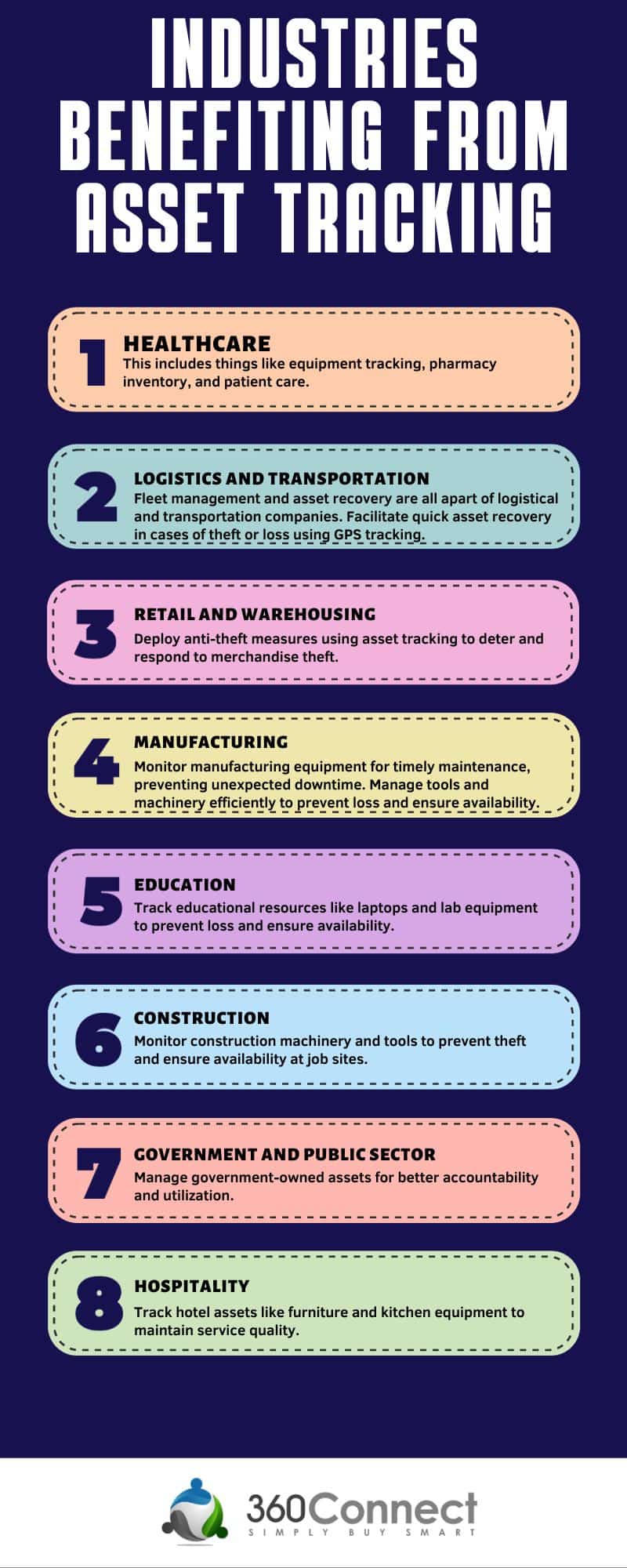
Choosing the Right Asset Tracking Solution
Not every company needs GPS tracking, and it’s important you find the right cost solution for you. Here’s a breakdown of some of your options.
RFID-based Systems:
Ideal for tracking high-value assets or large volumes of items. RFID tages are small smart labels that store various information and multiple tags and be scanned at once. Generally do not require Wi-Fi or cellular connectivity as they use local RFID readers. However, the data collected is often transferred to a central system via a network connection.
Pros:
- Highly accurate and efficient in tracking
- Capable of reading multiple tags for multiple devices simultaneously
- Durable and can work in various environmental conditions
Cons:
- Higher initial setup costs compared to others listed below
- Limited read range, depending on the type of RFID
- Potential interference from metals and liquids
GPS Tracking Systems:
Best for tracking vehicles or assets in transit. Includes GPS devices secured to an asset that will transmit a signal and that’s how the asset tracking works. It requires cellular capabilities for real-time tracking data transmission. GPS tracking system would be best for industries that need to track high-value equipment.
Pros:
- Provides precise location tracking, ideal for mobile assets.
- Global coverage.
- Useful for route optimization and geofencing.
Cons:
- Less effective indoors.
- Higher power consumption.
- Ongoing costs due to cellular data usage.
Barcode Systems:
Cost-effective for tracking inventory or lower-value assets. They are perfect for companies that need to track low-value tools and assets. You’ll scan the barcode to track when the item is used and who has the item checked out. Does not require WiFi or cellular connectivity for scanning, but data transfer to central systems may require a network connection.
Pros:
- Cost-effective and easy to implement.
- Wide range of applications and easy to customize.
- Simple to use with minimal training.
- Barcodes can be scanned with mobile devices
Cons:
- Requires line-of-sight for scanning.
- Can be prone to damage or wear, affecting readability.
- Manual scanning can be time-consuming for large inventories.
Bluetooth Low Energy Beacons:
BLE beacons continuously emit a radio signal that can be received by Bluetooth-enabled devices such as smartphones, tablets, or dedicated receivers. The signal they emit includes unique identifiers, which can be used to determine the beacon’s location or trigger specific actions in the receiving device. They may run for months or even years on a single charge, making them ideal for long-term deployments that do not require frequent maintenance. BLE beacons typically do not require Wi-Fi or cellular connectivity for basic operations but may use these for data transfer or advanced functionalities.
Pros:
- Low energy consumption, extending the life of battery-powered tags.
- Good for indoor tracking and proximity sensing.
- Can be integrated with smartphones and other smart devices.
Cons:
- Limited range compared to GPS.
- Signal can be affected by physical barriers.
- Less precise than GPS for outdoor tracking.
Some other factors to consider are user-friendliness, cost, and whether or not the system will integrate with the technology you already have.
Need Asset Tracking for Your Business?
Don’t worry, 360Connect has got your back! We help customers find high-quality suppliers every day. Just fill out our 1-2 minute form and we’ll contact you to verify your information and needs. From there, up to 5 suppliers will reach out to you with quotes. This process is 100% free and easy to use!
